Updated 7/23/25
Despite numerous blogs and speculation, EDI is not dead. It is never going to die, and stands as the most efficient communication and data management tool for B2B transactions. Well, what is EDI? Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard format. More importantly, it’s a crucial tool in modern business communications, offering a range of benefits that enhance data accuracy, reduce costs, and speed up business processes. Let’s explore the fundamentals of electronic data interchange, its benefits, common standards and protocols, and how to implement it in your business. Additionally, we’ll touch on future trends that could shape the landscape of EDI, but never kill it.
Table of Contents
- What is EDI?
- How Does an EDI System Work?
- Electronic Data Interchange Business Process Benefits
- Types of EDI Solutions
- Risks and Challenges
- Understanding EDI Mapping
- Common EDI Standards, Documents and Protocols
- Implementing EDI Integration in Your Business
- The Future of Electronic Data Interchange
What is EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange refers to the electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in a (hopefully) standardized format. Non-standard EDI is a different blog article. Unlike traditional paper-based communication, EDI allows for the seamless transfer of documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices directly between computer systems. Furthermore, EDI compliance is required across myriad industries.
Electronic data interchange plays a pivotal role in modernizing and streamlining business transactions. It facilitates faster, more accurate, and secure exchanges of information by replacing paper business documents. This shift not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual data entry. Some cost estimates go as high as $10 per order for manual order entry, which is directly off your bottom line. Traditionally, businesses in various industries relied on physical paper-based documents for transactions, which could be prone to errors, delays, and inefficiencies caused by manual data entry and time-consuming manual processes. EDI eliminates these issues by converting paper documents into electronic documents in a standard format that can be directly integrated into a company’s ERP or business systems (like D365 , Acumatica , NetSuite , or CloudSuite ). This automates and expedites the entire transaction process, whether order-to-cash or procure-to-pay.
How Does an EDI System Work?
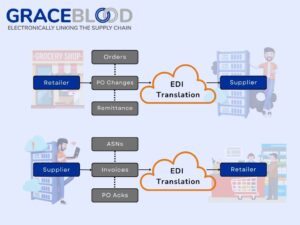
Any proper electronic data interchange definition would not be complete without explaining how it works. Business data is converted into a standardized format as part of data preparation in EDI. This involves extracting relevant information from internal systems and formatting it according to the latest standards, which are determined and updated by the Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) organization . The most current standard version is 8010, released in 2020. The goal is to ensure that the data is structured and organized in a way that can be universally understood.
The EDI data is transmitted to the recipient through a secure communication channel once it is prepared. EDI uses various protocols for data transmission, including AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), and HTTP/S (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). These protocols ensure that the data is sent securely and reliably. The electronic document is integrated into the recipient’s business systems and a functional acknowledgment is sent. This step parses the data and maps it to the appropriate fields within the company’s internal systems, such as the ERPs mentioned above. This integration helps in automating business processes and reducing manual intervention.
Electronic Data Interchange Business Process Benefits
EDI minimizes the risk of errors by automating data entry and processing. Since EDI documents are exchanged in a standardized electronic format, the need for manual input is reduced, leading to fewer mistakes and more accurate information. Business transactions are processed almost instantly compared to the delays associated with paper-based documents. This speed leads to quicker order fulfillment, faster invoicing, and overall improved efficiency in business processes and supply chain workflows.
EDI reduces printing, postage, and storage costs by essentially eliminating paper. Additionally, the automation of document processing decreases the need for manual labor, resulting in significant cost savings for businesses. Electronic data interchange facilitates timely and accurate communication between trading partners. Therefore, this improved information exchange helps build stronger trading partner relationships by ensuring that all parties have access to the same data and can respond quickly to changes or issues.
Types of EDI Solutions
When choosing an EDI solution, businesses typically consider two main deployment models: on-premise EDI translation software and cloud-based EDI. Each offers distinct advantages and considerations based on factors such as company size, budget, IT capabilities, and operational needs.
On-Premise EDI Translator
An on-premise system is hosted and maintained in-house by the organization’s IT team. This model is generally preferred by larger enterprises that require full control over their data and system configurations.
Pros:
- Greater control over infrastructure and security protocols.
- Customization options tailored to unique business processes.
- Integration flexibility with legacy systems.
Cons:
- High upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT resources.
- Longer deployment times and more complex upgrades.
- Requires ongoing maintenance and dedicated staff.
Cloud-Based EDI
Cloud-based (or hosted) solutions are managed by third-party providers and accessed through the internet. This model is ideal for small to mid-sized businesses or those seeking scalability and simplified management. Typically, support and maintenance services are handled by the EDI provider.
Pros:
- Lower initial costs and predictable subscription-based pricing.
- Faster implementation with minimal IT involvement.
- Easy scalability to support business growth or seasonal fluctuations.
Cons:
- Limited customization compared to on-premise solutions.
- Potential concerns over data ownership and vendor dependency.
- May require additional safeguards for integration with on-site systems.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your organization’s priorities, IT infrastructure, budget, and long-term growth strategy.
Risks and Challenges
While EDI provides significant benefits in automation, efficiency, and accuracy, its implementation and maintenance come with notable challenges. Understanding these risks is crucial for successful adoption.
- Data Security: As EDI transmission involved sensitive business documents, ensuring encryption, secure protocols, and compliance with industry regulations is critical to avoid data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Evolving Standards: EDI standards such as ANSI X12 and EDIFACT frequently evolve. Keeping systems and mappings up to date to ensure compatibility can be demanding, especially in global trade environments.
- Implementation Complexity: Initial setup can be complex, involving mapping, data integration with internal systems (e.g., ERP or WMS), and coordination with multiple trading partners.
- Trading Partner Dependency: Smooth operation often depends on partners’ EDI readiness and adherence to agreed standards. Misalignments can lead to failed transactions or delays.
- System Management: Even after deployment, EDI systems require ongoing monitoring, updates, and error handling. This includes managing acknowledgments, rejected transactions, and troubleshooting communication issues.
Address these challenges with the right tools, resources, and expert guidance and you’ll go far in maintaining a resilient and efficient environment.
Understanding EDI Mapping
EDI mapping is the process of translating data between a company’s internal systems and the standardized EDI formats required by trading partners. It ensures that the EDI file contains required fields such as invoice data, dates, and product codes and that they are are correctly aligned between systems, enabling accurate and automated document exchange. Effective mapping reduces errors, improves processing speed, and helps maintain compliance with partner specifications. Additionally, mapping can be done using in-house EDI software or outsourced to EDI providers who offer pre-built templates and ongoing support to manage changes in partner requirements.
Common EDI Standards, Documents and Protocols
Several EDI message standards and protocols are commonly used to ensure compatibility between different systems. ANSI X12 is widely used in North America, while EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport) is prevalent in Europe and other parts of the world. XML-based EDI is also gaining traction for its flexibility and compatibility with modern web technologies. EDI communication relies on various protocols to ensure secure and reliable data transfer. AS2 is a popular protocol that uses encryption for secure communication over the internet. FTP and HTTP/S are also used for transferring documents, with HTTP/S offering additional security features. Common documents, otherwise known as EDI transaction codes, include the Purchase Order (850), Invoice (810), Advance Ship Notice (856), and Purchase Order Acknowledgment (855). And these transaction sets allow businesses to automate key processes such as ordering, billing, shipping, and confirmation, improving efficiency and reducing manual errors.
Implementing EDI Integration in Your Business
Choosing a Solution Provider
Select an EDI solution provider that meets your business needs and budget. Consider factors such as ease of integration with existing business systems, user-friendliness, and the level of customer support offered when selecting an EDI service provider. You should also evaluate the scalability of the solution to accommodate future growth and evolving business needs.
Mapping Data
As part of integration, define how data from your internal systems—such as your ERP or order management systems—will be mapped to the appropriate EDI formats. This step is crucial for ensuring seamless data flow between your system and your trading partners. In addition, accurate mapping enables automated processing, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with partner specifications.
Testing
Ensure that data is accurately transmitted and received by conducting thorough testing of the entire EDI process. What’s more, testing helps identify and resolve any data transmission or integration issues before going live.
Consider factors such as ease of integration with existing systems, user-friendliness, and the level of customer support provided when selecting a provider. Furthermore, you should also valuate the scalability of the solution to accommodate future growth and changes in your business.
The Future of Electronic Data Interchange: Trends to Know
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of EDI and B2B integration. Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly popular for their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. APIs, which allows for real-time data exchanges is also gaining traction, allowing for immediate updates and responses. Additionally, we expect AI integration to automate complex tasks and improving data analysis. Electronic data interchange will play a crucial role in enabling seamless and efficient interactions between organizations as digital business transformation continues to evolve. The integration of advanced technologies and real-time capabilities will further enhance efficiency, solidifying its position as a cornerstone of modern business communications.
Ready to Embrace EDI? Unlock Greater Efficiency for Your Business
Electronic Data Interchange offers a wealth of benefits that can significantly enhance your business operations. By improving data accuracy, accelerating transaction processing, and reducing costs, EDI helps streamline business processes and foster better relationships with trading partners. Understanding “what is EDI?” and embracing B2B technology is a strategic move towards achieving greater efficiency and effectiveness in your business.
So are you ready to transform your business with electronic data interchange? Contact us for a free consultation and discover how our VelociLink™ solution can help you harness the power of EDI for your organization.